Database Connector
The Database connector establishes connectivity with a wide range of Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) relational Databases, enabling the execution of SQL operations. It allows the utilization of MEL expressions within connector fields and the dynamic configuration of attributes based on the specific Database configuration employed. This flexibility facilitates multi-tenant scenarios by adjusting connection attributes according to the information received from individual requests.
Various query types are supported, including predefined, dynamically constructed, and customizable template queries. Batch updates enable the execution of multiple SQL requests in a single operation, while Data Definition Language (DDL) requests modify the data structure without altering the data itself. The Database connector is an integral part of QuickIntegration.
To configure the Database connector:
- Define your Database’s location and connection details.
- Configure the operation you wish to perform.
- Include the query to execute on the Database.
Supported Commands
The Database connector offers support for the following commands:
- Select
- Insert
- Update
- Delete
Configuration
- Drag and drop the DB Connector
- Right click on connector, you can define the DB Connector configuration.
Quickintegrate Query Generator
- Click on the Query Generator icon.
- Choose the table name from the dropdown list to specify the source. We can set a limit on the number of records to retrieve.
- In the filters section, include conditions for the fields to be used in the query, employing operations such as NULL, NOT NULL, =, !=, etc. Your query will be generated based on these selections.
| Fields | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Table Name | DataBase Table Name | Customers |
| Your Generated Query is | DataBase Query | SELECT * FROM customers WHERE city =:city |
| Filters (Fields) | Particular field where DB will Operate | city |
| Filters (Operation) | Operations like NULL, NOT NULL, =, !=, etc | = |
Read Operation
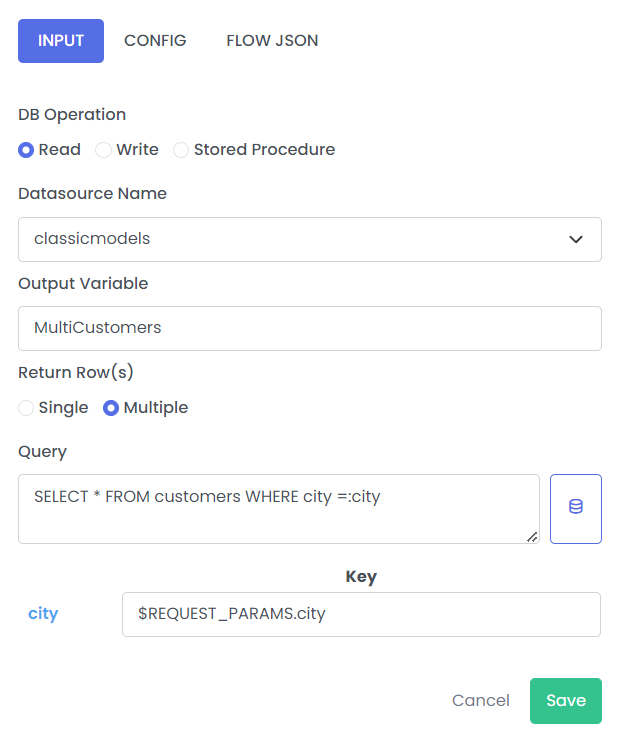
1. Get multiple row(s)
| Fields | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| DB Operation | Read / Write / Stored Procedure | Read |
| Datasource Name | Datasource Name which is configured in connection properties. Please refer the link for instructions on creating the datasource name | classicmodels |
| Return Row(s) | Single/Multiple | Multiple |
| Output Variable | Stores output of connections operations | MultiCustomers |
| Query | DataBase Query | SELECT * FROM customers WHERE city =:city |
| Gradle dependencies | Database driver dependencies which are configured in connection properties. Please refer the link for instructions on adding dependencies | com.mysql:mysql-connector-j:9.0.0 |
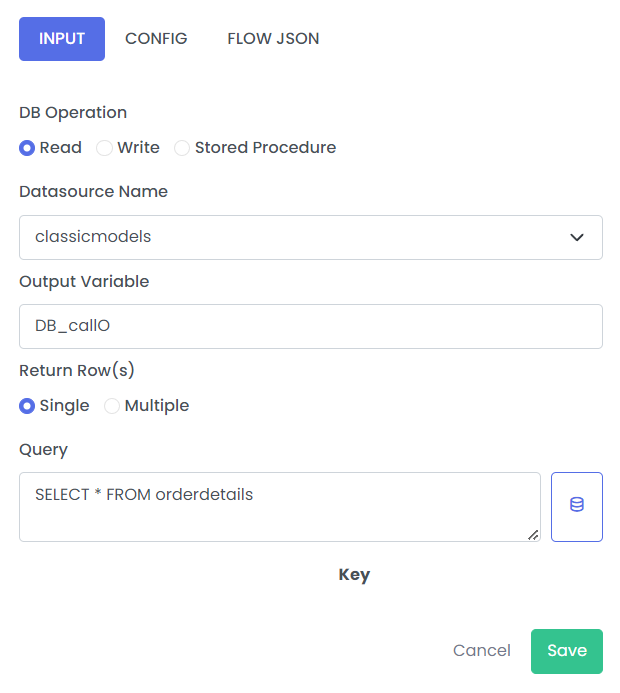
2. Get single row
Write Operation
When we need to modify records in the database, we can choose the Write option from the DB Operations menu.
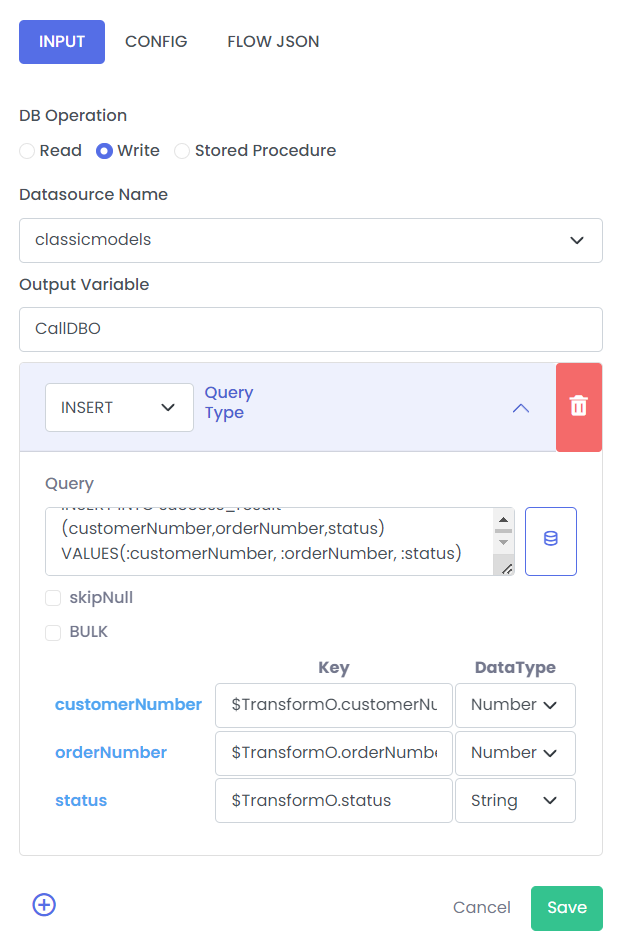
1. Normal Insert
The following shows a insert operation usage without checking:
- skipNull - Excludes
NULLvalues. - BULK - Performing a large number of data manipulation operations (insert, update, delete) in a single call
2. Skip Null
If skipNull is checked then it update the query on runtime and remove all the values from query for fields that contain NULL values.
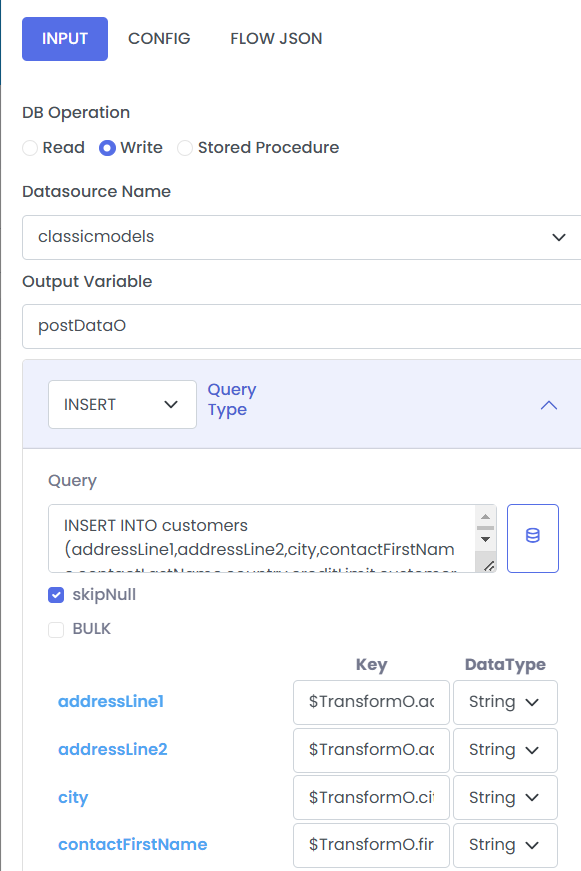
If there are any 'null' values while performing this query, those fields will be removed from the query execution. This helps best while performing update operation, where data loss can be avoided for previous record for important columns.
This works only in case of normal write operation and not in bulk.
3. Bulk Operations
Let's explore how to compose a delete query.
- Choose the query type as Delete from the dropdown list.
(Note: You can do similar for insert/update) - Check the bulk operation to delete multiple records using a single query
- Specify the fields for the delete condition.
- Check the Bulk checkbox below the query textbox. This specifies that we want to execute the query for bulk records.
- Now we will see the Parent textbox. Here we specify the list from the pipeline. eg. $MultiCustomers, which is the list of customers that we are fetching from the pipeline.
(Note: Needs to be java list object.)This list will contain map of customer. - Now that we got the list, we will do keys mapping. In the key section we specify the key we will get from the map object of the list metion in the Parent.
- Finally we will give the output name, which will contain the array of
0'sand1's.
Example of MultiCustomers
{
"MultiCustomers": [
{
"custNo": 1,
"custName": "Alice Johnson",
"custMobile": "1234567890"
},
{
"custNo": 2,
"custName": "Bob Smith",
"custMobile": "9876543210"
}
]
}
The above done config would like the image below.
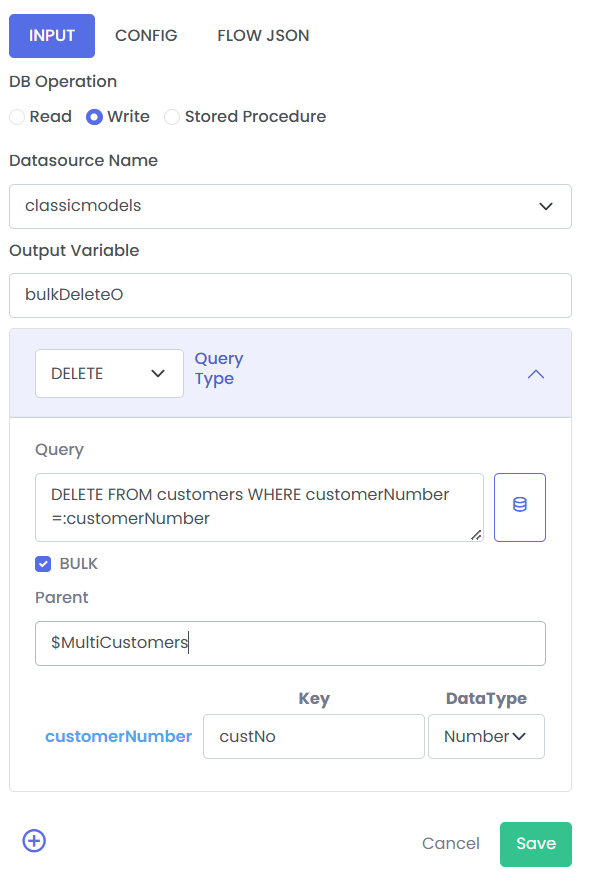
Here we gave the query for deleting the customer from customers table, for customerNumber. This will be bulk delete as we selected the query type DELETE and checked the Bulk. We also gave the Parent, $MultiCustomers, which is list of customers and we got this from the pipeline. After we mapped the customerNumber with the custNo we get from the each object from the list. We can also set which datatype the value will be.
This will delete all the customers from the table for the custNo in a single query execution.
| Fields | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| DB Operation | Read / Write / Stored Procedure | Write |
| Datasource Name | Datasource Name which is configured in connection properties. Please refer the link for instructions on creating the datasource name | classicmodels |
| Query Type(s) | Methods like INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE | DELETE |
| Output Variable | Stores output of query operations | bulkDeleteO |
| Parent | Defined by Using $ key word, followed by the varibale name in the pipeline. Contains the list of map objects from the pipeline. | $MultiCustomers |
| Gradle dependencies | Database driver dependencies which are configured in connection properties. Please refer the link for instructions on adding dependencies | com.mysql:mysql-connector-j:9.0.0 |
| Target | The target to be mapped on the query. | customerNumber |
| Key | The key to be retrieved from the map object from the list. | custNo |
| Data Type | The type of value data for the key. | Number |
While Bulk is checked, we cant use the skipNull.
Stored Procedure Operation
A stored procedure is a precompiled collection of SQL statements and optional control-of-flow statements that you can execute as a single unit to perform a specific task in a database.
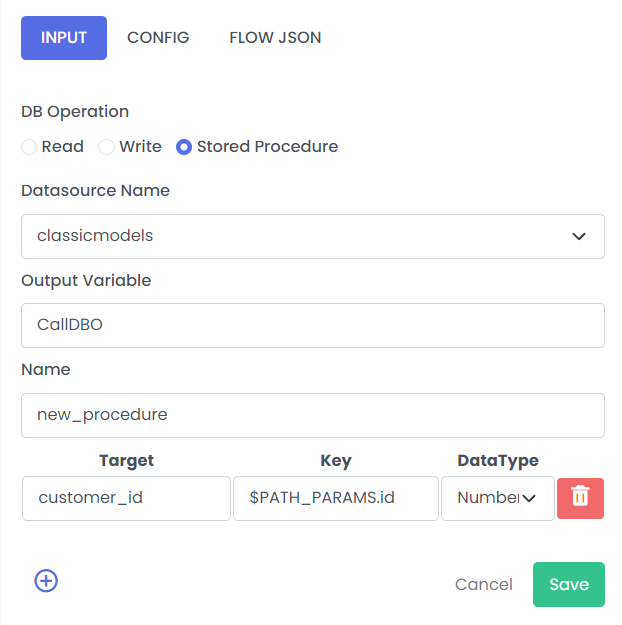
| Fields | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| DB Operation | Read / Write / Stored Procedure | Stored Procedure |
| Datasource Name | Datasource Name which is configured in connection properties. Please refer the link for instructions on creating the datasource name | classicmodels |
| Output Variable | Stores output of connections operations | CallDBO |
| Name | Procedure name | new_procedure |
| Gradle dependencies | Database driver dependencies which are configured in connection properties. Please refer the link for instructions on adding dependencies | com.mysql:mysql-connector-j:9.0.0 |
| Target | Parameter that is passed to procedure | customer_id |
| Key | Value of target | $PATH_PARAMS.id |
| DataType | Type like String / Number / Double / Boolean | Number |